 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
ABOUT FOREST DISTRICT
 Lasy nadleśnictwa, fot. Krzysztof Moroz
Lasy nadleśnictwa, fot. Krzysztof Moroz
 Lasy nadleśnictwa, fot. Mariusz Grondys
Lasy nadleśnictwa, fot. Mariusz Grondys
 Lasy nadleśnictwa, fot. Mariusz Grondys
Lasy nadleśnictwa, fot. Mariusz Grondys
Zielona Góra Forest District manages the area of over 17.000 ha of forests. It is highly interesting in terms of nature with rich flora and fauna.
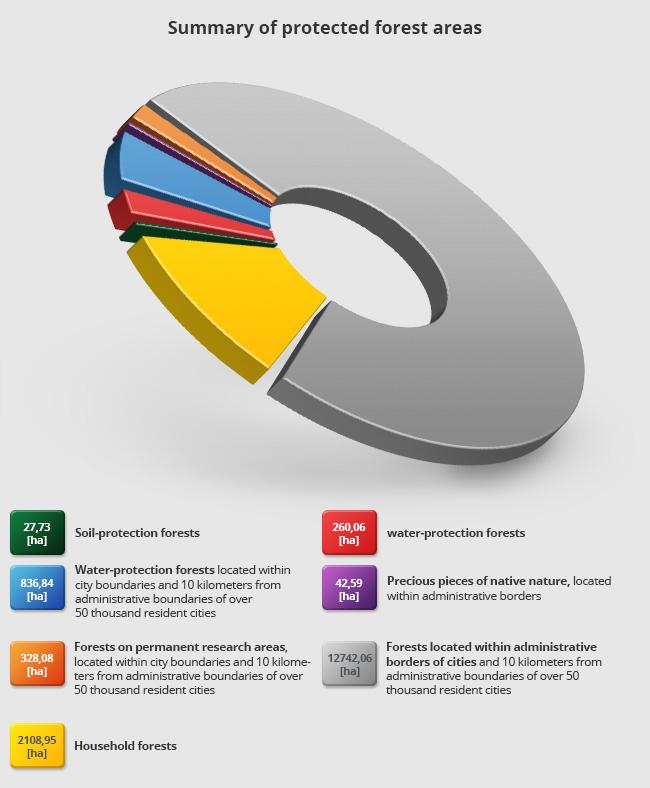
80% of forests managed by Zielona Góra Forest District are protective forests.
The area is characterised by a varied lie of the land and its forms. A particularly unique landform is the Embankment of Zielona Góra with Wilkanów Hill being the highest point in the whole district (221 metres above sea level). The surface of the Embankment is varied and its slopes are crossed by numerous hills and valleys of all shapes and sizes. Ranging from 100 to 220 metres above sea level running from east to west the Embankment is actually an end moraine dating back to mid-Polish ice age or even earlier (south-Polish).
The Czerwieńsk Height is characteristic for its sandy hills surrounding valleys of small rivers. In the areas of Czerwieńsk and Wysokie dune embankments with height difference up to a dozen metres exist. Northern and southern parts of the forest district are located in the valleys of rivers Odra and Śląska Ochla. The area is not varied, it is basically flat with little gradient (below 3%). To the south of Zielona Góra Embankment, there is a sandur which is 1-4 kilometres wide (between Letnica and Jędrzychów). It dates back to maximal stage of north-Polish ice age (Leszno stadial).
Zielona Góra Forest District woods are located in the Third Pomerania and Great Poland Land, Sixth Lubuskie Lake District in Ziemia Lubuska Mesoregion and in a part of forest complex referred to as the Lubuskie Forest. Fundamental elements of the landscape are the Hills of Zielona Góra in the form of mountain-range.
Surface area of Zielona Góra Forest District is 30.7 ha and is densely forested (up to 57,9%). The forests of the district consist of 130 forest complexes and the largest of them constitutes 90% of the managed area.
As far as area is concerned, forest complexes of 1-20 ha dominate (121 in total). Apart from the forests governed by the State Forests, woods of other forms of ownership (natural person and legal person) are situated within the area of the district - 777 ha in total.
Tree stands of the forest district comprise of 26 species, 22 of them are dominant. The most dominant is Scots pine (90% share) followed by oak, alder, black locust and birch. Participation level of the remaining species does not exceed 1% of forest surface. Single-storied stands with artificial regeneration dominate. The forests of Zielona Góra Forest District play a number of roles, the most important being protective function.
16 types of soil have been distinguished on the area of the forest district.
Overwhelming coniferous forest habitats with significant dominance of Scots pine indicate rather little variety of flora. It does not mean that they are less interesting. Fertile soils are associated with habitats with rich plant cover.
Apart from trees, forest flora ecosystem consists of shrubs and undergrowth. In the Zielona Góra forest district there are partly protected species: cup lichen, Iceland moss, lesser periwinkle, lily of the valley, common ivy, wintergreen, woodruff and fully protected such as: stag's-horn clubmoss, stiff clubmoss, common polypody, fox glove, snowdrops. Nature monuments, namely the most impressive trees of the forest district are also protected.
Fauna is equally impressive as flora and protected mammal species such as European beaver and barbastelle appear here. Protected invertebrate are represented by large coppers, Ophiogomphus cecilia and the large white-faced darter, amphibians represented by northern crested newt and the European fire-bellied toad. Many other species of different classes can be found.





